Tissues
Tissue
Tissue is a group of cells similar in structure and function /or work together to achieve a particular function forms a tissue.Study of tissues is called Histology.
Division of Labor/Cell specilization
In unicellular organism (Amoeba), single cell performs all basic functions, whereas in multi-cellular organisms (Plants and Animals) shows division of labour as Plant tissue & Animal tissues
Tissue Classified into two types
- Plant
- Animal
PLANT TISSUE

MERISTEMATIC TISSUE

- The growth of plants occurs only in certain specific regions as dividing tissue, also known as meristematic tissue, is located only at these points.
Structure
The cells of this tissue are very active, they have dense cytoplasm, thin cellulose walls and prominent nuclei. They lack vacuole.
Meristematic tissue are of three types with respect to where they are present in plant
- apical
- lateral
- intercalary
Apical
present at the growing tips of stems and roots and increases the length of the stem and the root.
Lateral
The girth of the stem or root increases due to lateral meristem (cambium).
Intercalary
It is the meristem at the base of the leaves or internodes (on either side of the node) on twigs.
PERMANENT TISSUE
The cells formed by meristematic tissue take up a specific role and lose the ability to divide. As a result, they form a permanent tissue.
This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a function is called differentiation.
Permanent tissue are further of two types
- Simple permanent
- Complex permanent
Simple permanent tissue are further of three types
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
Parenchyma-A few layers of cells form the basic packing tissue called parenchyma

- Are live cells.
- are loosely packed with large intercellular spaces.
- provides support to plants and also stores food.
- In some situations contains chlorophyll and performs photosynthesis, and then it is called chlorenchyma.
- In aquatic plants, large air cavities are present in parenchyma to give buoyancy to the plants to help them float Such a parenchyma type is called aerenchyma
- parenchyma of stems and roots also stores nutrients and water.
Collenchyma- These type of permanent tissue provides flexibility in plants.

- It allows easy bending in various parts of a plant (leaf, stem) without breaking.
- It also providesmmechanical support to plants.
- usually found in leaf stalks below the epidermis.
- Are live cells.
- They are elongated in shape and irregularly thickened at the corners.
- Have very little intercellular space.
Sclerenchyma-makes the plant hard and stiff, for example husk of a coconut.
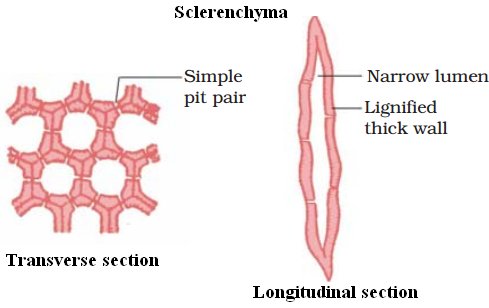
- It is made of sclerenchymatous tissue.
- The cells of this tissue are dead.
- Cells are long and narrow as the walls are thickened due to lignin (a chemical substance which acts as cement and hardens them).
- No internal space inside the cell due to thick wallls.
- Present in stems, around vascular bundles, in the veins of leaves and in the hard covering of seeds and nuts.
- It provides strength to the plant parts.
Guard cells & Epidermal tissue

The tissue aids in protection and exchange of gases.
Guard cells are kidney shaped in dicots, dumb bell shaped in monocots to guard the stomata. The epidermal tissues of roots aid in absorption of water and minerals. The epidermal tissues in desert plants have a thick waxy coating of Cutin with waterproof quality. The epidermal tissues form the several layer thick Cork or the Bark of the tree.
Complex tissues are made of more than one type of cells. All these cells coordinate to perform a common function

Complex permanent tissue are further of two types.
- Xylem
- Phloem
Xylem -consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres.
- Cells have thick walls, and many of them are dead cells.
- Tracheids and vessels are tubular structures. This allows them to transport water and minerals vertically.
- Xylem parenchyma stores food and helps in the sideways conduction of water.
- Fibres are supportive in function.
Phloem – is made up of four types of elements: sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and the phloem parenchyma
- Sieve tubes are tubular cells with perforated walls.
- Phloem is unlike xylem in that materials can move in both directions in it. Phloem transports food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
- Except for phloem fibres, phloem cells are living cells.
ANIMAL TISSUE

On the basis of the functions they perform we can think of different types of animal tissues, such as
- epithelial tissue,
- connective tissue,
- muscular tissue and
- nervous tissue
EPITHELIAL
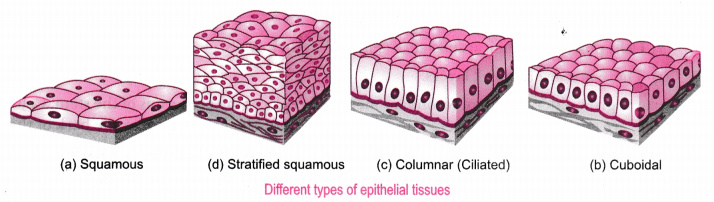
- The covering or protective tissues in the animal body are epithelial tissues.
- covers most organs and cavities within the body. It also forms a barrier to keep different body systems separate, eg skin, the lining of the mouth, the lining of blood vessels,lung alveoli and kidney tubules etc
- Tissue cells are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet. They do not have intercellular spaces.
Types of epithelial tissue
squamous epithelium-are extremely thin and flat and form a delicate lining
- skin of body,oesophagus and lining of the mouth are covered with squamous epithelium.
columnar (meaning ‘pillar-like’) epithelium- facilitates movement across the epithelial barrier
- absorption and secretion occur, as in the inner lining of the intestine.
- ciliated columnar epithelium- In the respiratory tract, the columnar epithelial tissue also has cilia, which are hair-like projections on the outer surfaces of epithelial cells. These cilia can move, and their movement pushes the mucus forward to clear it.
Cuboidal epithelium- (with cube-shaped cells) forms the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands.
- it provides mechanical support.
glandular epithelium- portion of the epithelial tissue folds inward, and a multicellular gland is formed.
MUSCULAR

- consists of elongated cells, also called muscle fibres. This tissue is responsible for movement in our body.
These are of three types such as.
- Striated muscles/skeletal muscles/voluntary muscles :
They are cylindrical, un-branched and multinucleated. They have dark bands and light bands.
- Unstriated muscles /smooth muscles/involuntary muscles:
They are commonly called as Smooth muscles, having no striations (dark bands/ light bands are absent). Commonly found alimentary canal, uterus, Iris of an Eye. They are spindle shaped. Involuntary in nature.
- Cardiac Muscles:
They are commonly called as Heart muscles, cylindrical, branched and uni-nucleate. Involuntary in nature
CONNECTIVE

The cells of connective tissue are loosely spaced and embedded in an intercellular matrix . The matrix
may be jelly like, fluid, dense or rigid.
Different connective tissues are-
a) Blood: The Blood is a fluid connective tissue.
- Blood plasma has RBCs (Red Blood Cells) WBCs (White Blood Cells) and platelets.Blood plasma contains proteins, salts and hormones.
- Blood flows and transports gases, digested food, hormones and waste materials.
b) Bone: The bone is a connective tissue with hard matrix, composed of calcium and phosphorus.
- It forms the framework that supports the body.
- It also anchors the muscles and supports the main organs of the body.
- It is a strong and non flexible tissue.
- A bone is connected by another bone with another connective tissue called ligaments which is very elastic and it has considerable strength and contain very little matrix.
- A bone is connected by muscle with another connective tissue called tendon which are fibrous tissue with great strength but limited flexibility.
c) Cartilage: The cartilage is a connective tissue with solid matrix composed of proteins and sugars.
- It has widely spaced cells.
- It smoothens bone surfaces at joints.
- It is commonly seen in nose, ear, trachea, and larynx.
d) Areolar Connective Tissue: It is found between the skin and muscles, around the blood vessels.
- It fills nthe space inside the organs, supports internal organs
- It supports internal organs and aids in repair of tissues.
e)Adipose Connective Tissue: It is filled with fat globules for the storage of fat. It acts as insulator.
NERVOUS

- The tissue responds to stimuli.
- The brain, spinal cord and nerves are composed of nervous tissue or neurons.
- A neuron consists of Cell Body, cytoplasm, Nucleus, Dendrite, Axon, nerve ending.
- The neuron impulse allow us to move our muscles when we want to respond to stimuli.
- Many nerve fibres bound together by connective tissue make up a nerve.
1. Presence of tissues in a multicellular organisms ensures:
(a) Faster development
(b) Division of labour
(c) Higher reproductive potential
(d) Body strength
ANS-(b)
2. Parenchyma: Simple: Phloem: …………..
(a) Simple
(b) Collenchyma
(c) Complex
(d) Xylem
ANS-(c)
3. Which of the following statements given below is correct about meristematic tissue?
(a) Is made of cells that are incapable of cell division
(b) Is made of cells that are capable of cell division
(c) Is composed of single type of cells
(d) Is composed of more than one type of cell
ANS-(b)
4. The nuclei of meristematic cells are:
(a) Small
(b) Large
(c) Medium sized
(d) None of these
ANS-(b)
5. The cell wall of meristematic cell is made of:
(a) Protein
(b) Amino acid
(c) Peptidoglycan
(d) Cellulose
ANS-(d)
6)Which of the following tissues has dead cells?
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Collenchyma
(d) Epithelial tissue
ANS-(b)
7)Find out incorrect sentence
(a) Parenchymatous tissues have intercellular spaces
(b) Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners
(c) Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues
(d) Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles
ANS-(c)
8)Girth of stem increases due to
(a) apical meristem
(b) lateral meristem
(c) intercalary meristem
(d) vertical meristem
ANS-(b)
9)Which cell does not have perforated cell wall?
(a) Tracheids
(b) Companion cells
(c) Sieve tubes
(d) Vessels
ANS-(b)
10)Intestine absorb the digested food materials. What type of epithelial cells are responsible for that?
(a) Stratified squamous epithelium
(b) Columnar epithelium
(c) Spindle fibres
(d) Cuboidal epithelium
ANS-(b)
